What is Feathr?
Feathr is the feature store that is used in production in LinkedIn for many years and was open sourced in April 2022. Read our announcement on Open Sourcing Feathr and Feathr on Azure.
Feathr lets you:
- Define features based on raw data sources (batch and streaming) using pythonic APIs.
- Register and get features by names during model training and model inferencing.
- Share features across your team and company.
Feathr automatically computes your feature values and joins them to your training data, using point-in-time-correct semantics to avoid data leakage, and supports materializing and deploying your features for use online in production.
Feathr Highlights
- Scalable with built-in optimizations. For example, based on some internal use case, Feathr can process billions of rows and PB scale data with built-in optimizations such as bloom filters and salted joins.
- Rich support for point-in-time joins and aggregations: Feathr has high performant built-in operators designed for Feature Store, including time-based aggregation, sliding window joins, look-up features, all with point-in-time correctness.
- Highly customizable user-defined functions (UDFs) with native PySpark and Spark SQL support to lower the learning curve for data scientists.
- Pythonic APIs to access everything with low learning curve; Integrated with model building so data scientists can be productive from day one.
- Rich type system including support for embeddings for advanced machine learning/deep learning scenarios. One of the common use cases is to build embeddings for customer profiles, and those embeddings can be reused across an organization in all the machine learning applications.
- Native cloud integration with simplified and scalable architecture, which is illustrated in the next section.
- Feature sharing and reuse made easy: Feathr has built-in feature registry so that features can be easily shared across different teams and boost team productivity.
Running Feathr on Azure with 3 Simple Steps
Feathr has native cloud integration. To use Feathr on Azure, you only need three steps:
- Get the
Principal IDof your account by runningaz ad signed-in-user show --query id -o tsvin the link below (Select “Bash” if asked), and write down that value (something likeb65ef2e0-42b8-44a7-9b55-abbccddeefff). Think this ID as something representing you when accessing Azure, and it will be used to grant permissions in the next step in the UI.
- Click the button below to deploy a minimal set of Feathr resources for demo purpose. You will need to fill in the
Principal IDandResource Prefix. You will need “Owner” permission of the selected subscription.
- Run the Feathr Jupyter Notebook by clicking the button below. You only need to change the specified
Resource Prefix.
Installing Feathr Client Locally
If you are not using the above Jupyter Notebook and want to install Feathr client locally, use this:
pip install feathr
Or use the latest code from GitHub:
pip install git+https://github.com/linkedin/feathr.git#subdirectory=feathr_project
Feathr Examples
Please read Feathr Capabilities for more examples. Below are a few selected ones:
Rich UDF Support
Feathr has highly customizable UDFs with native PySpark and Spark SQL integration to lower learning curve for data scientists:
def add_new_dropoff_and_fare_amount_column(df: DataFrame):
df = df.withColumn("f_day_of_week", dayofweek("lpep_dropoff_datetime"))
df = df.withColumn("fare_amount_cents", df.fare_amount.cast('double') * 100)
return df
batch_source = HdfsSource(name="nycTaxiBatchSource",
path="abfss://feathrazuretest3fs@feathrazuretest3storage.dfs.core.windows.net/demo_data/green_tripdata_2020-04.csv",
preprocessing=add_new_dropoff_and_fare_amount_column,
event_timestamp_column="new_lpep_dropoff_datetime",
timestamp_format="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
Defining Window Aggregation Features
agg_features = [Feature(name="f_location_avg_fare",
key=location_id, # Query/join key of the feature(group)
feature_type=FLOAT,
transform=WindowAggTransformation( # Window Aggregation transformation
agg_expr="cast_float(fare_amount)",
agg_func="AVG", # Apply average aggregation over the window
window="90d")), # Over a 90-day window
]
agg_anchor = FeatureAnchor(name="aggregationFeatures",
source=batch_source,
features=agg_features)
Define features on top of other features - Derived Features
# Compute a new feature(a.k.a. derived feature) on top of an existing feature
derived_feature = DerivedFeature(name="f_trip_time_distance",
feature_type=FLOAT,
key=trip_key,
input_features=[f_trip_distance, f_trip_time_duration],
transform="f_trip_distance * f_trip_time_duration")
# Another example to compute embedding similarity
user_embedding = Feature(name="user_embedding", feature_type=DENSE_VECTOR, key=user_key)
item_embedding = Feature(name="item_embedding", feature_type=DENSE_VECTOR, key=item_key)
user_item_similarity = DerivedFeature(name="user_item_similarity",
feature_type=FLOAT,
key=[user_key, item_key],
input_features=[user_embedding, item_embedding],
transform="cosine_similarity(user_embedding, item_embedding)")
Define Streaming Features
Read the Streaming Source Ingestion Guide for more details.
Point in Time Joins
Read Point-in-time Correctness and Point-in-time Join in Feathr for more details.
Running Feathr Examples
Follow the quick start Jupyter Notebook to try it out. There is also a companion quick start guide containing a bit more explanation on the notebook.
Cloud Architecture
Feathr has native integration with Azure and other cloud services, and here’s the high-level architecture to help you get started. 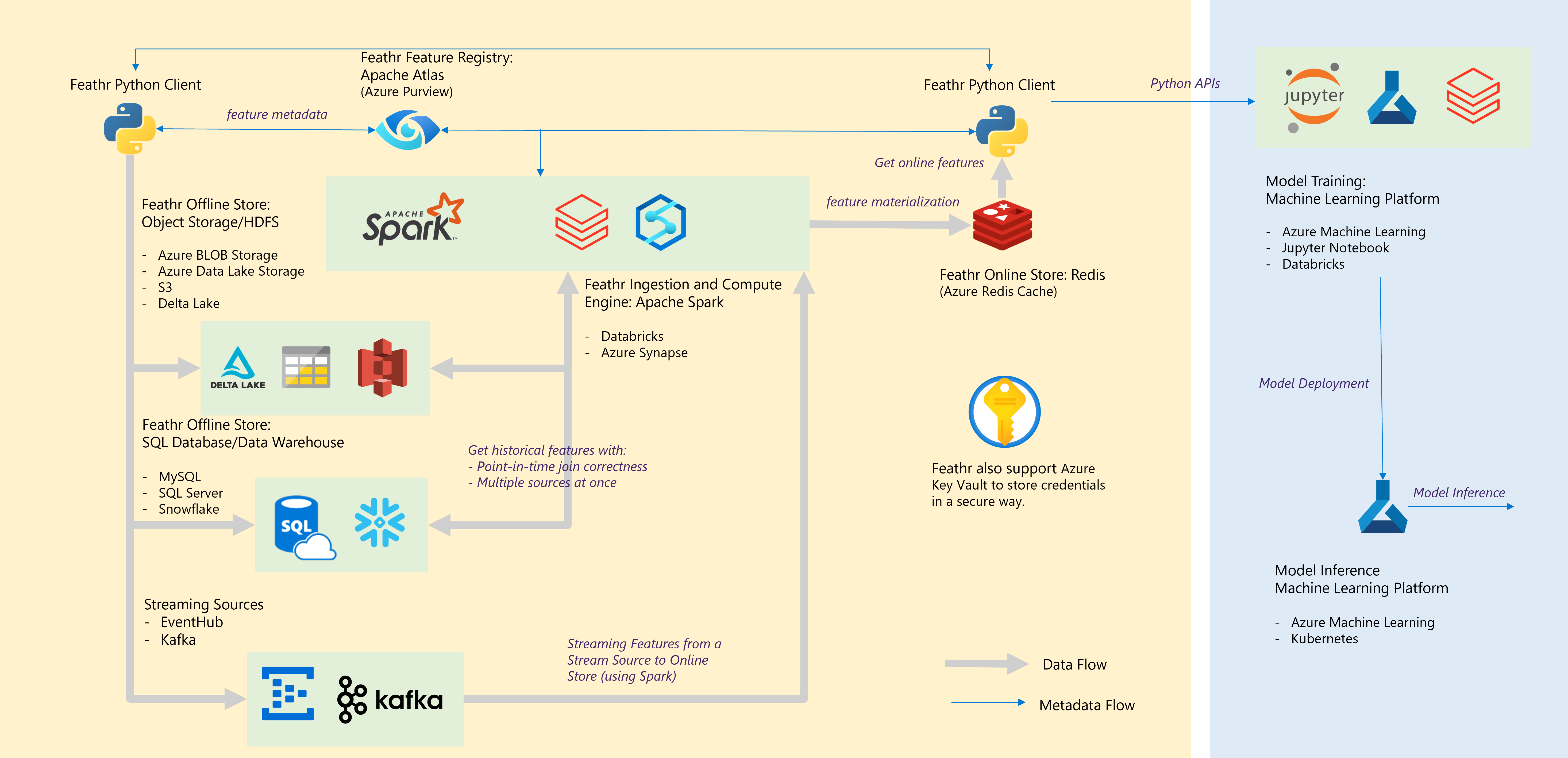
Next Steps
Quickstart
Concepts
How-to-guides
- Azure Deployment
- Local Feature Testing
- Feature Definition Troubleshooting Guide
- Feathr Expression Language
- Feathr Job Configuration